§ NOI-Online-T1-序列

其实这道题是全场最难的……
我这里给出一种并查集的做法。
首先我们把操作2中的 和 合并
对于操作1我们可以把他转化为操作2来做。
比如我们针对操作1给出 和 两条边,对 进行同增,对 进行同减。
这样就变成了 了。
然后我们把操作2缩点,然后把操作1的边连到操作2缩的点上。
然后对操作1合并。
此时,图中的每个点的度数最多为一。
那么对于一条边 如果 那么就是YES;
对于一个自环 如果 为偶数,那么就是YES;
对于一个度数为零的点 如果 那么就是YES;
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
char buf[1 << 21], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define gc() getchar()
#else
#define gc() (p2 == p1 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
#endif
#define is_number (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
template < typename Type >
void read(Type& a) {
a = 0; bool f = 0; char ch;
while (!(ch = gc(), is_number)) if (ch == '-') f = 1;
while (is_number) a = (a << 3) + (a << 1) + (ch ^ '0'), ch = gc();
a = (f ? -a : a);
}
template < typename Type, typename... Args >
void read(Type& t, Args&... args) {
read(t), read(args...);
}
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 5;
int T, n, m, vis[MAXN];
int u[MAXN], v[MAXN];
int a[MAXN], b[MAXN];
int nxt[MAXN], to[MAXN];
int head[MAXN], tot;
struct UnionFindSet {
int fa[MAXN];
void init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
fa[i] = i;
}
int find(int x) {
if (x ^ fa[x]) fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
return fa[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
int u = find(x);
int v = find(y);
if (u ^ v) {
fa[v] = u;
a[u] += a[v];
b[u] += b[v];
}
}
} ufs;
void add(int x, int y) {
to[++tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
}
signed main() {
for (read(T); T; --T) {
read(n, m);
tot = 0;
memset(head, 0, sizeof head);
ufs.init(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(b[i]);
for (int i = 1, opt; i <= m; ++i) {
read(opt, u[i], v[i]);
if (opt ^ 1) vis[i] = 1, ufs.merge(u[i], v[i]), --i, --m;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
add(ufs.find(u[i]), ufs.find(v[i]));
add(ufs.find(v[i]), ufs.find(u[i]));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int t = ufs.find(to[head[i]]);
for (int x = nxt[head[i]]; x; x = nxt[x])
ufs.merge(t, ufs.find(to[x]));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (head[i]) {
int x = ufs.find(i);
int y = ufs.find(to[head[i]]);
if (x ^ y) {
if ((a[x] - b[x]) ^ (a[y] - b[y])) {
puts("NO");
goto there;
}
}
else {
if ((a[x] - b[y]) & 1) {
puts("NO");
goto there;
}
}
}
else if (ufs.fa[i] == i) {
if (a[i] ^ b[i]) {
puts("NO");
goto there;
}
}
}
puts("YES");
there: ;
}
}
§ NOI-Online-T2-冒泡排序
这道题我在考场上的做法很玄,本来是奔着40pts的部分分去的,结果爆零了(至今没找到原因)
我们设
显然逆序对数量为
于是问题就转化为了动态维护 。
手玩几组数据后我们可以发现,每轮冒泡 都会有一下的变化:
于是树状数组维护即可
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
char buf[1 << 21], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define gc() getchar()
#else
#define gc() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
#endif
#define is() (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
template < typename Type >
void read(Type& a) {
a = 0; bool f = 0; char ch;
while (!(ch = gc(), is())) if (ch == '-') f = 1;
while (is()) a = (a << 3) + (a << 1) + (ch ^ '0'), ch = gc();
a = (f ? -a : a);
}
template < typename Type, typename... Args >
void read(Type& t, Args&... args) {
read(t), read(args...);
}
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 5;
int n, m, bigger[MAXN], bucket[MAXN], a[MAXN];
long long bit[MAXN], init_inver_tot;
void Update(int x, long long y) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x) bit[x] += y;
}
long long GetAnswers(int x) {
long long res = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x) res += bit[x];
return res;
}
signed main() {
read(n, m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(a[i]), init_inver_tot += (bigger[i] = i - 1 - GetAnswers(a[i])), bucket[bigger[i]]++, Update(a[i], 1);
memset(bit, 0, sizeof bit), Update(1, init_inver_tot), init_inver_tot = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) init_inver_tot += 1LL * bucket[i], Update(i + 1 + 1, init_inver_tot - n);
for (int i = 0, op, x; i < m; ++i) {
read(op, x);
if (n - 1 < x) x = n - 1;
if (op ^ 2) {
if (a[x + 1] > a[x]) {
swap(a[x], a[x + 1]);
swap(bigger[x], bigger[x + 1]);
Update(1, 1);
Update(bigger[x + 1]++ + 2, -1);
}
else {
swap(a[x], a[x + 1]);
swap(bigger[x], bigger[x + 1]);
Update(1, -1);
Update(--bigger[x] + 2, 1);
}
}
else printf("%lld\n", GetAnswers(x + 1));
}
return 0;
}
§ NOI-Online-T3-最小环
全场最水的一道题,但是可怕的心理作用还是让我放弃了这道题。
首先有一个显然的结论,我们需要把这 个数分为 个环。
虽说是显然但是不画画图还真的玩不动
给一下图示意一下:
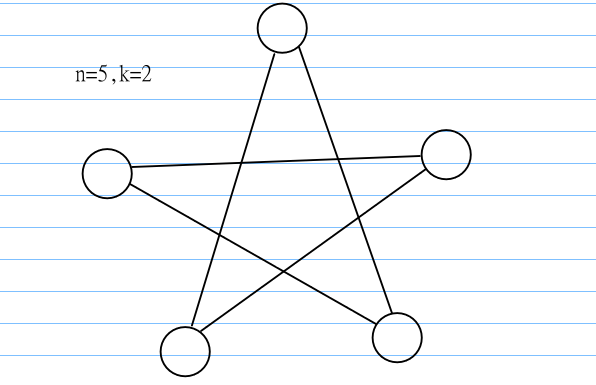
图中那个看起来像个五角星的东西其实就是个环
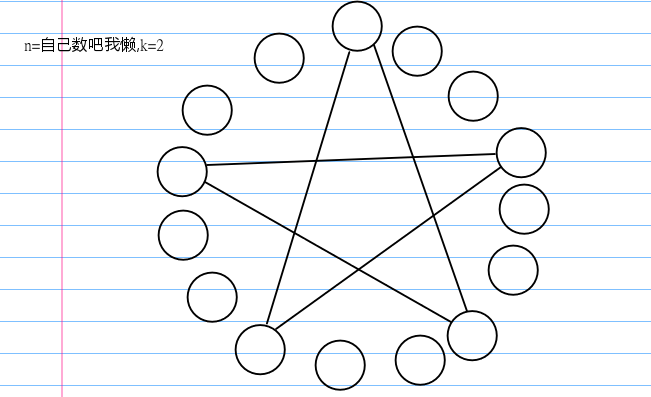
这个图中有 个环,这就是我们的结论。
具体到实现,我们采用的是预处理出所有答案。
还有 的情况需要特殊处理一下
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 5e5 + 5;
vector < int > integer(MAXN);
vector < long long > ans(MAXN);
int gcd(int x, int y) {
return !y ? x : gcd(y, x % y);
}
signed main() {
int n, k;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &integer.at(i)), ans.at(0) += (long long)integer.at(i) * (long long)integer.at(i);
sort(integer.begin() + 1, integer.begin() + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= (n >> 1); ++i) {
if (!(n % i)) {
int t = n / i;
vector < int > process(MAXN);
int tot = 0;
for (int j = 2; j < t; j += 2) process.at(++tot) = j;
process.at(++tot) = t;
for (int j = t - 1 - (t & 1); j > 0; j -= 2) process.at(++tot) = j;
for (int j = t + 1; j <= n; ++j) process.at(j) = process.at(j - t) + t;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
if (!(j % t)) ans.at(i) += (long long)integer.at(process.at(j)) * (long long)integer.at(process.at(j + 1 - t));
else ans.at(i) += (long long)integer.at(process.at(j)) * (long long)(integer.at(process.at(j + 1)));
}
}
for (int i = 0, x; i < k; ++i) scanf("%d", &x), printf("%lld\n", ans.at(x ? gcd(n, x) : 0));
return 0;
}
§ 总结
(其实我不是很会写这玩意儿)
果然心理素质还是不行……错过了T3这样的水题。
总体来说,把握住机会,把题目都当作大白菜(雾)。
然后就是多去做题吧,题量多少都不嫌多。
就这样(
§ 普及组口胡
说了是口胡所以没代码不保证正确/xyx
至于题目难度这是NOIOL不是NOIpOL给了搬出题人放飞自我的空间。
T1:普通NOIp普及难度,各位巨佬随便切
T2: 基础多项式,会的人就很套路。不会的话就n方dp骗骗分
T3: 这道题我不太确定,应该是Floyd+矩阵。
完结撒六花